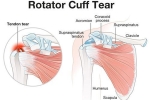
Does PRP Enhance Rotator Cuff Surgery/Healing?

Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has been investigated as a treatment for various musculoskeletal injuries, including rotator cuff tears. The effectiveness of PRP for healing rotator cuff tears is still a subject of ongoing research and debate. Here’s a detailed look at the current understanding of PRP therapy in the context of rotator cuff tears:
What is PRP Therapy?
PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of a patient’s own platelets into an injured area to promote healing. Platelets release growth factors that are believed to accelerate tissue repair and regeneration.
PRP for Rotator Cuff Tears
Mechanism of Action
- Growth Factors: PRP contains growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), which can promote cell proliferation, tissue repair, and new blood vessel formation.
- Inflammation Reduction: PRP may help reduce inflammation, thereby creating a more favorable environment for healing.
Application in Rotator Cuff Tears
- Non-Surgical Treatment: PRP injections are sometimes considered for partial rotator cuff tears or tendinopathy to reduce pain and facilitate healing.
- Surgical Augmentation: PRP is used during surgical repair of rotator cuff tears to enhance the healing process and improve outcomes.
Current Evidence and Research
Efficacy in Non-Surgical Treatment
- Mixed Results: Studies on the use of PRP for non-surgical treatment of rotator cuff tears show mixed results. Some patients report reduced pain and improved function, while others see no significant benefit.
- Pain Relief: Some evidence suggests that PRP may provide short-term pain relief and improve shoulder function, particularly in patients with tendinopathy or partial tears.
Efficacy in Surgical Augmentation
- Enhanced Healing: Some studies indicate that PRP can enhance the healing of the rotator cuff when used during surgical repair. PRP may improve tendon-to-bone healing and reduce the risk of re-tear.
- Inconsistent Outcomes: Other studies show no significant difference in healing rates or functional outcomes when PRP is used during rotator cuff surgery compared to surgery without PRP.
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- Conflicting Results: Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of clinical trials report conflicting results. Some reviews find modest benefits of PRP in reducing pain and improving function, while others conclude that the evidence is insufficient to support routine use of PRP.
Clinical Considerations
Patient Selection
- Individual Variation: The effectiveness of PRP may vary based on factors such as the size and severity of the tear, patient age, activity level, and overall health.
- Partial vs. Full-Thickness Tears: PRP may be more beneficial for partial tears or tendinopathy than for full-thickness rotator cuff tears.
Procedure Protocols
- Lack of Standardization: There is no standardized protocol for PRP preparation and administration, leading to variability in platelet concentrations and clinical outcomes.
- Injection Technique: The technique and site of PRP injection can also influence its effectiveness.
Conclusion and Recommendations
While PRP therapy holds promise for the treatment of rotator cuff tears, the evidence remains mixed. Here are some recommendations:
- Consult with Specialists: Patients considering PRP for rotator cuff tears should consult with orthopedic specialists to understand the potential benefits and limitations.
- Evidence-Based Approach: Treatment decisions should be based on the latest evidence and tailored to the individual patient’s condition and needs.
- Combination Therapies: PRP may be more effective when combined with other treatments, such as physical therapy or surgical repair.
- Further Research: Continued research and well-designed clinical trials are needed to clarify the role of PRP in rotator cuff tear treatment and establish standardized protocols.
Summary
PRP therapy may offer benefits for some patients with rotator cuff tears, particularly for pain relief and possibly enhancing healing when used during surgery. However, the overall effectiveness and best practices for PRP treatment are still under investigation. Patients should seek personalized medical advice and consider current evidence when exploring PRP therapy for rotator cuff tears.